About CD4IR
The United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA) approved the conduct of the Research on Cybersecurity for Development in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (CD4IR) on 3rd August, 2022. The Research was led by Dr Jimson Olufuye with Data Collation support from Timilehin Ambali, Ismaila Lamidi and John Olufuye.
This Research provided evidence of a positive relationship between Cybersecurity and Development in the Fourth Industrial Revolution which commenced in 2011 and the ramifications continue to accelerate geometrically as a result of giganet (broadband) engendered Internet of all Things and innovations.
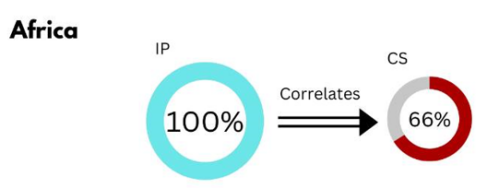
In-depth analyses with 40 countries showed Cybersecurity in Africa has a strong correlation of about 66% with Internet Penetration for which Internet Penetration exhibits a measure of Cybersecurity, confidence and trust in the use of cyberspace for general business operations. In Latin America and Asia/Middle-East, it is 60% and 82% respectively.
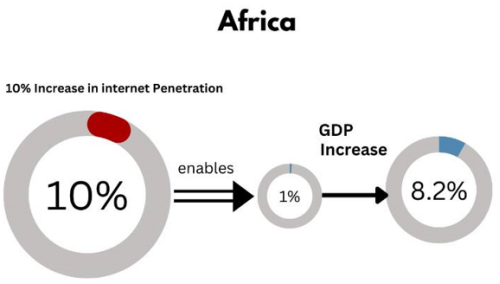
Results indicated that a 10% increase in Internet Penetration enables between 1% and 8.2% increase in GDP per capita in Africa while it enables between 3% and 5.1% in Latin America and between 5.5% and 12% in Asia/Middle-East over the period under consideration - 2011 to 2021; and with the sample space of 40 countries in Africa and 15 countries in Latin-America and Asia/Middle-East. When the top 15 countries in Africa are considered, IP enables between 4.8% and 7.4% increase in GDP per capita.
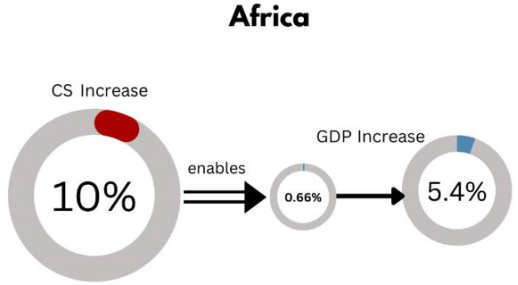
As Internet Penetration and Cybersecurity go hand-in-hand, results also indicated that Cybersecurity has good correlation with GDP and when data is computed using the sample space of 40 countries for Africa, the result showed that a 10% rise in Cybersecurity maturity enables between 0.66% and 5.4% increase in GDP per capita in Africa.
The result is between 3.36% and 5.18% increase in GDP per capita following a 10% increase in Cybersecurity maturity when 15 top African countries are used in the computation. In Latin America, CS enables between 1.8% and 3% increase in GDP per capita; while in Asia/Middle-East, it enables between 4.5% and 9.8% increase in GDP per capita over the period under consideration - 2011 to 2021; and with the sample space of 15 countries in each of Latin-America and Asia/Middle-East.
Published Internet cyber-attacks and financial losses in Africa during the period 2011-2021 amounted to 873million and $20billion respectively. By estimates, the numbers recorded are less than 10% of the actual assuming non-disclosure of many incidents in the absence of legal requirements for disclosure. In Latin-America, the number of attacks and financial losses are 181million and $128billion respectively. In Asia/Middle-East, the number of attacks and financial losses are 131 million and $30billion respectively.
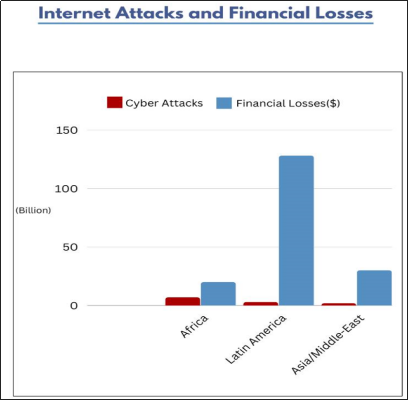
Although, data showed of the 3 regions, Latin-America suffered the highest financial losses due to cyber-attacks, Africa at 29.1% has the weakest Cybersecurity maturity index followed by Latin America at 35.6% and Asia at 61% which is the strongest with the lowest financial losses per capita.

It thus implied that the stronger a nation’s cybersecurity posture, the lower the financial losses per capita. Nations therefore need to take cybersecurity seriously to reduce losses if not completely eliminate it.
The overall Research results underscored the importance of Cybersecurity to Development in the Fourth Industrial Revolution and UNECA’s commitment to strengthening Cybersecurity in Africa, evidenced in the outcome of the March, 2022 Lome Cybersecurity Summit of Heads of States with the “Lome Declaration” and the establishment of the African Centre for the Coordination and Research in Cybersecurity (ACCRC).
The report outlined the methodology for the conduct of the Research which included the use of most recent (up to June 2022) Internet Penetration data in top forty (40) African countries, top fifteen (15) countries in each of Asia/Middle-East and Latin America to provide the basis to explore the correlation of Cybersecurity indices with Gross Domestic Products (GDP) over a period of at least ten (10) years (2011 - 2021); and to further make the case for countries to take Cybersecurity more seriously as an enabler of development in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR).
